How to operate a drone safely and effectively is more than just mastering the controls; it’s about understanding the technology, adhering to regulations, and prioritizing safety. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills needed to confidently take to the skies, from pre-flight checks and airspace awareness to mastering flight maneuvers and capturing stunning aerial footage. We’ll cover everything from basic controls to advanced flight planning, ensuring you’re prepared for a safe and rewarding drone experience.
This comprehensive guide breaks down the process into manageable steps, covering essential pre-flight procedures, detailed explanations of drone controls and operation, strategic flight planning techniques, capturing high-quality aerial imagery, and post-flight maintenance. We also delve into the crucial aspects of drone regulations and legal considerations to ensure responsible and compliant operation.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for safe and efficient drone operation. This involves inspecting key components, understanding local regulations, and briefing yourself on emergency procedures. Neglecting these steps can lead to accidents or legal issues.
Drone Pre-Flight Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection ensures your drone is in optimal condition. This systematic check minimizes the risk of malfunctions during flight.
| Component | Check | Acceptable Result | Unacceptable Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Inspect for cracks, damage, or loose fittings. | Intact propellers, securely fastened. | Cracked, chipped, or loose propellers. |
| Battery | Check battery level and condition. Ensure proper connection. | Sufficient charge, no visible damage. | Low charge, swollen battery, loose connection. |
| Camera | Verify camera functionality and lens clarity. | Clear image, proper focus. | Blurry image, lens obstruction. |
| Gimbal (if applicable) | Check for smooth movement and proper operation. | Smooth, stable gimbal movement. | Jerky movement, gimbal malfunction. |
| GPS Signal | Confirm a strong GPS signal is acquired. | Multiple satellites acquired, good signal strength. | Weak or no GPS signal. |
| Radio Control System | Test the responsiveness of the controller. | Responsive controls, no lag. | Unresponsive controls, significant lag. |
Understanding Airspace Restrictions

Operating a drone requires awareness of airspace regulations. Unauthorized flights in restricted areas can result in penalties.
Airspace is classified into different categories, each with specific rules. For example, Class G airspace typically allows recreational drone flights, while Class B airspace (around major airports) usually requires prior authorization. Understanding these classifications is paramount for safe and legal drone operation. Always check with your local aviation authority for specific regulations in your area.
Drone Safety Briefing
A safety briefing is essential for new drone operators. This covers potential hazards and emergency procedures to ensure safe operation.
- Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
- Avoid flying near people, buildings, or other obstacles.
- Be aware of weather conditions and avoid flying in adverse weather.
- In case of emergency, immediately initiate a return-to-home (RTH) maneuver or bring the drone down safely.
- Familiarize yourself with your drone’s emergency stop procedures.
Battery Safety and Charging
Proper battery handling is crucial for safety and longevity. Lithium polymer (LiPo) batteries used in drones require careful attention.
- Always use the manufacturer-recommended charger.
- Never leave LiPo batteries unattended while charging.
- Store LiPo batteries in a fire-resistant container.
- Do not overcharge or discharge LiPo batteries.
- Inspect batteries regularly for any signs of damage (swelling, leaks).
Drone Controls and Operation: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding basic drone controls and operating modes is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will cover the fundamental controls, different operating modes, and best practices for takeoff, landing, and navigation.
Basic Drone Controls
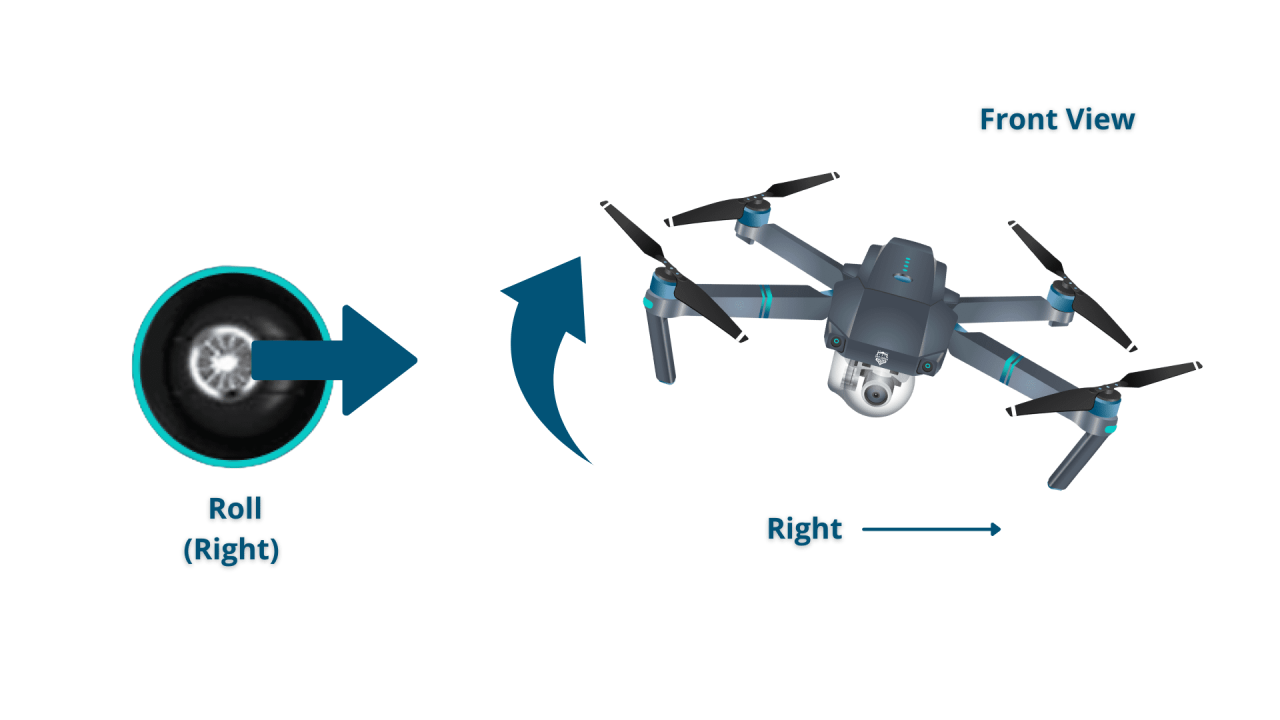
Standard drones typically use four primary controls: throttle, yaw, pitch, and roll. Mastering these controls allows for precise maneuvering.
- Throttle: Controls the drone’s altitude. Increasing throttle raises the drone, decreasing it lowers it.
- Yaw: Controls the drone’s rotation around its vertical axis (turning left or right).
- Pitch: Controls the drone’s movement forward or backward.
- Roll: Controls the drone’s movement left or right.
Drone Control Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability, catering to different skill levels and situations.
| Mode | Capabilities | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Beginner Mode | Simplified controls, limited speed and maneuverability, enhanced stability. | Less control over precise movements, restricted flight options. |
| Advanced Mode | Full control over all movements, higher speed and maneuverability. | Requires greater skill and precision, increased risk of accidents. |
| GPS Mode | Autonomous flight features, return-to-home functionality, precise positioning. | Relies on GPS signal strength, may not be effective in areas with weak signals. |
Safe Takeoff and Landing Procedures
Smooth and controlled takeoffs and landings are essential for preventing damage to the drone and ensuring safety.
- Ensure a clear and safe area for takeoff and landing.
- Check the battery level and GPS signal.
- Slowly increase the throttle to lift the drone vertically.
- Maintain a steady altitude and slowly move the drone to your desired location.
- For landing, slowly decrease the throttle until the drone gently touches down.
Navigating Different Environments
Navigating various environments requires adapting your flight techniques to maintain safety and achieve desired results.
- Open Fields: Easier navigation, focus on maintaining altitude and direction.
- Urban Areas: Increased complexity, requires awareness of obstacles and airspace restrictions. Prioritize safety and legal compliance.
- Near Obstacles: Maintain a safe distance, use obstacle avoidance features (if available), and proceed cautiously.
Flight Planning and Navigation
Careful flight planning is crucial for safe and efficient drone operations. This involves considering various factors, utilizing GPS technology, and employing obstacle avoidance strategies.
Drone Flight Planning Process
Before each flight, plan your route, considering wind speed, battery life, potential hazards, and airspace restrictions. This ensures a safe and productive flight.
- Check weather conditions (wind speed, direction).
- Assess battery life and plan a flight duration within its capacity.
- Identify potential hazards (obstacles, people, restricted areas).
- Plan your flight path, including waypoints and altitudes.
- Consider emergency landing options.
Utilizing GPS Coordinates and RTH
GPS coordinates allow for precise flight path planning, while the return-to-home (RTH) function ensures a safe return in case of signal loss or other emergencies.
Many drones allow you to input GPS coordinates to define waypoints for your flight. This enables you to create a precise flight path. The RTH function automatically guides the drone back to its takeoff point, providing a safety net in challenging situations. Always ensure a strong GPS signal before relying on RTH.
Obstacle Avoidance and Safe Distances
Maintaining safe distances from obstacles and other aircraft is crucial for preventing accidents. Utilize available technologies and practice good judgment.
- Use obstacle avoidance features (if available) on your drone.
- Maintain a safe distance from people and structures.
- Be aware of other aircraft and avoid conflicting airspace.
- Plan your flight path to minimize the risk of collisions.
Sample Flight Plan
This is a hypothetical example. Always adapt your flight plan to the specific circumstances of your mission.
Mission: Aerial photography of a park.
Waypoints:
Waypoint 1: Takeoff (34.0522° N, 118.2437° W, 10m altitude)
Waypoint 2: Over the lake (34.0530° N, 118.2445° W, 20m altitude)
Waypoint 3: Over the playground (34.0540° N, 118.2450° W, 20m altitude)
Waypoint 4: Return to Home (34.0522° N, 118.2437° W, 10m altitude)
Drone Camera and Image Capture
Understanding your drone’s camera features and settings is essential for capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos. This section covers camera specifications, different shooting modes, and techniques for optimizing image quality.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics, such as pre-flight checks and maneuvering, is crucial. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects from takeoff to landing, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Mastering these skills will allow you to confidently and safely operate your drone for various applications.
Drone Camera Features
Drone cameras vary in specifications. Common features include resolution (measured in megapixels for photos), field of view (how much of the scene is captured), and image stabilization (reducing camera shake).
Higher resolution generally means more detail in your images. A wider field of view captures a broader perspective, while image stabilization is crucial for sharp, clear footage, especially during flight.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource to help you understand this process is available at how to operate a drone. This comprehensive guide covers everything from safety regulations to advanced maneuvering techniques, ensuring you’re well-prepared for safe and responsible drone operation.
Ultimately, proficient drone operation requires both theoretical knowledge and practical experience.
Camera Modes and Settings
Most drones offer various shooting modes (photo, video, timelapse) and settings (ISO, shutter speed, aperture) to control image quality and creative expression.
- Photo Mode: Captures still images.
- Video Mode: Records moving images.
- Timelapse Mode: Creates a sequence of images over time, which can be compiled into a video.
Understanding settings like ISO (light sensitivity), shutter speed (duration the sensor is exposed to light), and aperture (controls the amount of light entering the lens) is vital for achieving the desired exposure and depth of field.
Achieving Optimal Image Quality
Adjusting camera settings allows you to fine-tune your images and videos, adapting to different lighting conditions and creative visions.
- Low Light: Increase ISO, but be mindful of increased noise (grain).
- Bright Light: Decrease ISO to avoid overexposure.
- Fast Movement: Increase shutter speed to freeze motion.
- Shallow Depth of Field: Use a wider aperture (lower f-stop number).
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media

Mastering composition and lighting techniques enhances the visual appeal of your aerial photography and videography.
- Composition: Use the rule of thirds, leading lines, and other compositional techniques.
- Lighting: Shoot during the golden hour (sunrise and sunset) for soft, warm light.
- Steady Shots: Avoid jerky movements; use smooth, controlled maneuvers.
- Post-Processing: Use editing software to enhance your images and videos.
Post-Flight Procedures and Maintenance
Post-flight procedures and regular maintenance ensure the longevity and performance of your drone. This includes inspecting components, storing batteries correctly, and performing routine cleaning and calibration.
Post-Flight Drone Inspection
After each flight, inspect your drone for any damage or issues. Proper storage of batteries and cleaning are also crucial steps.
- Inspect propellers, arms, and body for damage.
- Check for loose screws or connections.
- Clean the drone body and camera lens gently.
- Store the batteries properly in a designated storage container.
- Ensure the drone and accessories are stored in a dry, safe location.
Regular Drone Maintenance
Regular maintenance prolongs the life of your drone and ensures its optimal performance. This includes cleaning, calibration, and firmware updates.
- Cleaning: Regularly clean the drone body, propellers, and camera lens.
- Calibration: Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) periodically.
- Firmware Updates: Keep your drone’s firmware updated for improved performance and bug fixes.
Safe Storage of Drone and Accessories
Proper storage protects your drone and its accessories from damage and theft.
- Store the drone in a protective case or bag.
- Keep the batteries in a fire-resistant container.
- Store the remote controller and other accessories in a safe place.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Problems
Identifying and addressing common drone problems helps prevent more serious issues.
- Battery Issues: Check battery levels, connections, and condition.
- GPS Problems: Ensure a strong GPS signal; recalibrate if necessary.
- Control Issues: Check controller batteries and connections.
- Motor Problems: Inspect motors for damage or obstructions.
Understanding Drone Regulations and Laws
Operating a drone legally requires understanding and adhering to both national and local regulations. This includes registration, permit requirements, and penalties for violations.
Key Aspects of Drone Regulations, How to operate a drone
Drone regulations vary by country and region. Familiarize yourself with the specific laws governing drone operation in your area.
Generally, regulations cover areas such as registration requirements, airspace restrictions, flight limitations (altitude, distance), and operational guidelines. These regulations are in place to ensure public safety and prevent interference with manned aircraft.
Drone Registration and Permits
Many jurisdictions require drone registration and may require permits for specific operations, particularly in controlled airspace or for commercial purposes.
Registration usually involves providing information about the drone and its owner. Permits may be necessary for commercial operations, flights in restricted airspace, or specific types of drone activities. Always check your local aviation authority’s website for specific requirements.
Penalties for Violating Drone Regulations
Violating drone regulations can result in fines, legal action, and even criminal charges. Understanding the consequences is crucial for responsible operation.
Penalties can range from warnings and fines to more severe legal repercussions, depending on the severity of the violation. These penalties can be significant, emphasizing the importance of compliance.
Summary of Common Drone Regulations
| Regulation | Description | Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Registration | Registering your drone with the relevant authority. | Legal requirement for operation; failure to register may result in penalties. |
| Airspace Restrictions | Limitations on flying in certain airspace (e.g., near airports). | Violations may lead to fines or legal action. |
| Visual Line of Sight | Maintaining visual contact with the drone during flight. | Essential for safe operation; loss of visual contact can lead to accidents. |
| Maximum Altitude | Restrictions on how high you can fly your drone. | Exceeding the maximum altitude can result in penalties. |
| Weight Limits | Limitations on the weight of drones that can be operated without additional permits. | Heavier drones may require additional licenses or permissions. |
Operating a drone responsibly and skillfully requires a combination of technical proficiency, adherence to regulations, and a commitment to safety. By following the guidelines Artikeld in this guide, you’ll be well-equipped to enjoy the thrill of aerial flight while minimizing risks. Remember that continuous learning and practice are key to becoming a proficient and safe drone pilot. Embrace the journey, and happy flying!
FAQ Summary
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with beginner modes are available. Look for features like GPS assisted flight and automatic return-to-home functionality.
How long does a drone battery last?
Battery life varies greatly depending on the drone model and flight conditions. Check your drone’s specifications for estimated flight times.
What happens if I lose signal with my drone?
Most modern drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function that will automatically bring the drone back to its starting point if signal is lost. However, always fly within visual line of sight.
Do I need insurance for my drone?
Drone insurance is highly recommended, especially for commercial use, to cover potential damages or accidents.
Where can I find information on local drone regulations?
Check your local government’s website or contact your national aviation authority for specific regulations in your area.
